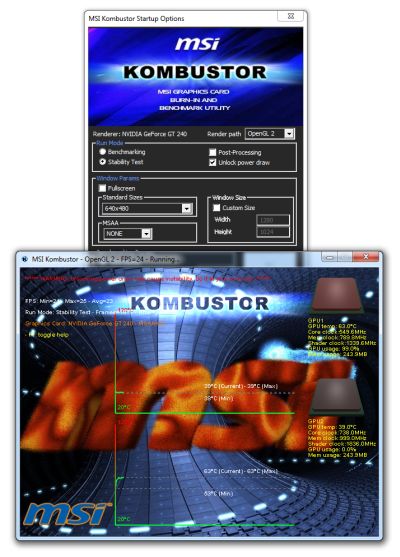
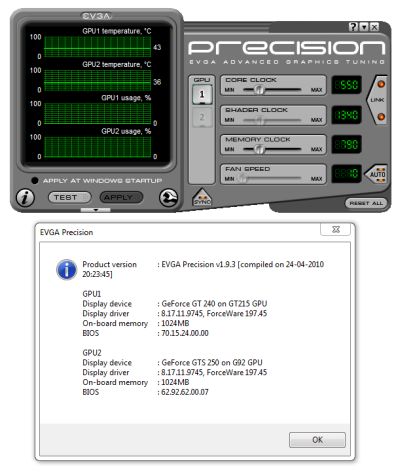
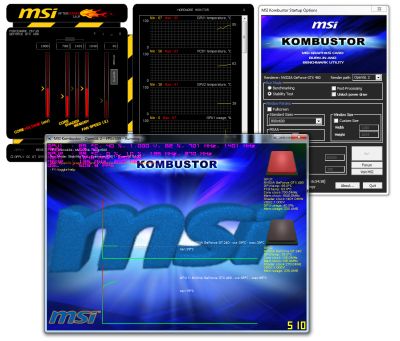
![EVGA GeForce GTX 580 Superclocked GPU Overclocking Session]()
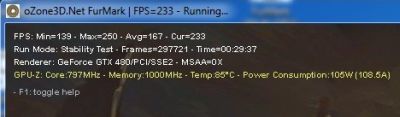
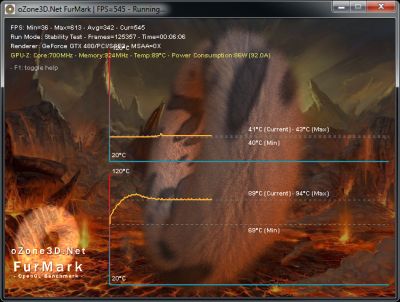
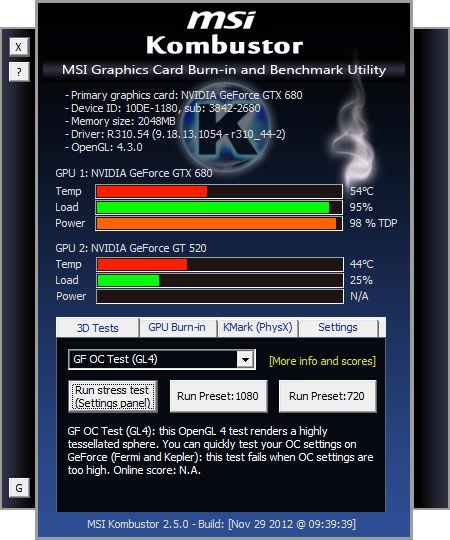
I just stress-tested with FurMark 1.9.0 my EVGA GTX 580 SC, overclocked at 900MHz with a Vcore (or VDDC or GPU voltage) of 1.100V. At first glance, the card was stable, no visual artifacts, a very high GPU temperature (96°C) with an insane power consumption: 385W for the card alone!
I even ran 3DMark11 without problem: P6534 and X2218.
I also launched Unigine Heaven 2.1 Direct3D 11 test (1920×1080, tessellation normal, 16X aniso, 4X MSAA): FPS: 52.9, Scores: 1333
But in Heaven, I noticed few visual artifacts. Then I launched an artifact scanning with the latest EVGA OC Scanner 1.6.0 and actually, 900MHz was a bit too high. Let’s see how to find stable and robust overclocking settings thanks to OC Scanner.
Test bench
- CPU: Core i7 960 @ 3.2GHz
- RAM: 4GB DDR3 Corsair Dominator
- Motherboard: GIGABYTE X58-A UD5
- Windows 7 64-bit
- Graphics drivers: R266.58
- PSU: Corsair AX1200
![Corsair AX1200 power supply unit]()
A high quality PSU, like Corsair’s AX1200, is important for overclocking a high-end graphics card like the GTX 580
First thing to do for overclocking a GTX 580 is to disable the over current protection (OCP). I simply used the latest GPU-Z 0.5.1 with the /gtx500ocp option (for information, FurMark 1.9.0 makes this step simpler).
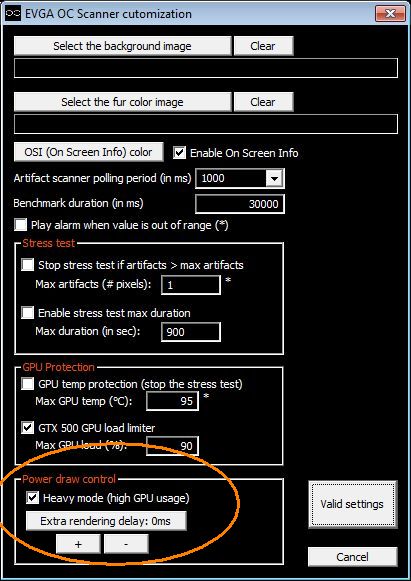
To detect artifacts with OC Scanner, I recommend to enable the heavy mode, in the settings box:
![EVGA OC Scanner, settings box]()
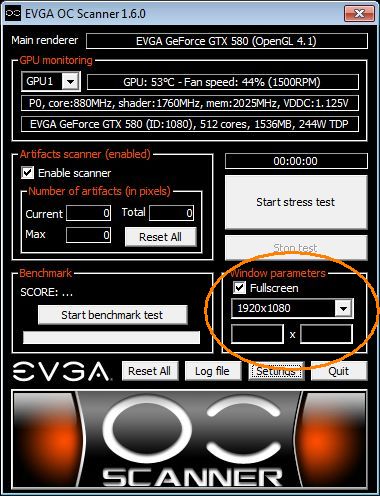
Then set the high resolution like 1920×1080 fullscreen:
![EVGA OC Scanner]()
Okay OC Scanner is ready for artifacts scanning. Press the Start stress test button and you should see this rendering:
![EVGA OC Scanner, GTX 580 SC]()
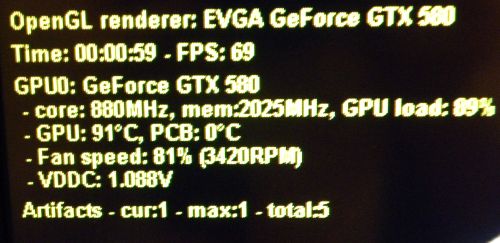
The most important line is the last one:
Artifacts: cur:0 - max:0 - total:0
In short, as long as all values are 0, that means you overclocking is stable. As soon as one value is greater than 0, your overclocking settings are too high:
![EVGA OC Scanner artifacts, GTX 580 SC]()
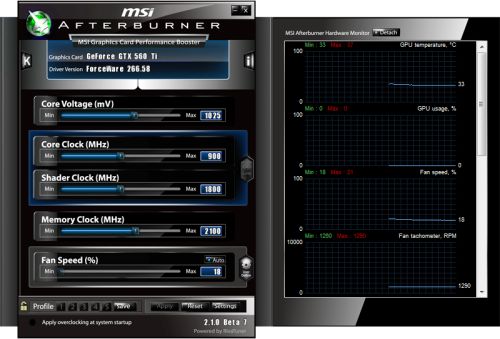
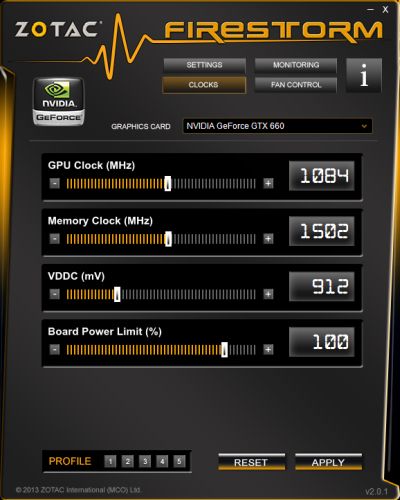
Here are the different steps of my GTX 580 overclocking (I set the core clock and core voltage with Afterburner 2.1.0 beta 7 –with Afterburner, 1.138V is the max GPU voltage we can set):
- 1 – GPU @ 890MHz, VDDC @ 1.113V –> 4 artifacts dectected after 1 min
- 2 – GPU @ 890MHz, VDDC @ 1.125V –> 2 artifacts dectected after 2 min
- 3 – GPU @ 890MHz, VDDC @ 1.138V –> 2 artifacts dectected after 7 min
- 4 – GPU @ 880MHz, VDDC @ 1.138V –> 1 artifact dectected after 4 min
- 5 – GPU @ 880MHz, VDDC @ 1.125V –> 1 artifact dectected after 15 min
- 6 – GPU @ 880MHz, VDDC @ 1.113V –> 1 artifact dectected after 3 min
- 7 – GPU @ 880MHz, VDDC @ 1.088V –> 5 artifacts detected after 1 min
- 8 – GPU @ 870MHz, VDDC @ 1.088V –> 2 artifacts detected after 1 min
- 9 – GPU @ 870MHz, VDDC @ 1.100V –> 1 artifact detected after 4 min
- 10 – GPU @ 870MHz, VDDC @ 1.125V –> no artifact detected after 15 min
![EVGA OC Scanner artifacts, GTX 580 SC]()
A you can see, OC Scanner is able to detect very small artifacts: few pixels in a full HD scene. Those few pixels are undetectable with our eyes in 3D scenes and that explains why I thought my OC was stable at 900MHz!
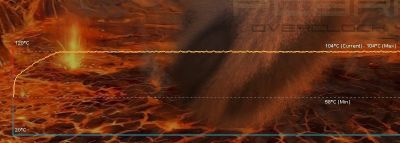
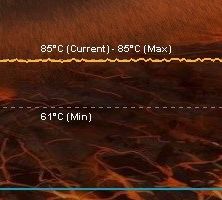
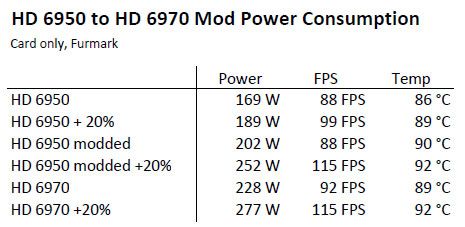
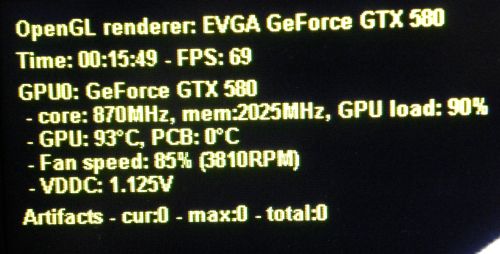
With these settings {870MHz, 1.125V}, the GPU temperature reaches 93°C and the power consumption of the testbed is 525W under OC Scanner. The power consumption of the testbed at idle is 120W and the PSU efficiency factor is around 0.9: (525-120) * 0.9 = 364W for the EVGA GTX 580 SC alone.
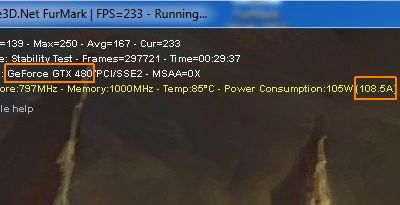
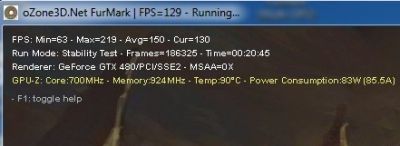
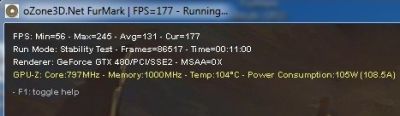
I validated these overclocking settings with a FurMark 1.9.0 burn-in test session (1920×1080 fullscreen, 15min): GPU: 98°C, fan speed 85% (3810RPM), total power consumption: 540W: (540-120)*0.9 = 378W for the GTX 580 alone!
![EVGA GTX 580 SC, stress-tested by FurMark 1.9.0]()
378W ? Is it not too much? Sure my friend, it’s too much, this is even a very, ultra high value for the power consumption of a graphics card . NVIDIA says the TDP of a GTX 580 is… 240W. The GTX 580 has one 8-pin + one 6-pin power connectors leading to a max of 300W for the board (see here for more details: Maximum Power Consumption of Graphics Card Connectors). Then we are completely out of range with 378W! That’s why you have to have a solid PSU, a solid motherboard to overclock a high-end graphics card.
3DMark11 and Unigine Heaven scores with the new OC settings {870MHz, 1.125V}:
- 3DMark11: P6391
- Unigine Heaven 2.1: FPS: 51.7 , Scores: 1303
With a GPU core clocked at 870MHz and fed with a voltage of 1.125V, EVGA’s GTX 580 SC is stable. Finding the best overclocking settings for a GPU is a rather long process. And if you want to be sure that your OC settings are stable, I recommend you to burn your GPU with FurMark, or EVGA OC Scanner for at least one hour. After what, play with your favorite game to be sure the OC is okay.
EVGA’s GTX 580 SC deserves this nice badge:
![EVGA GTX 580 SC, FurMark approved!]()
A detail about RTI tc. RTI tc is the Return To Idle time constant. This time constant is the time required for a reduction of 63% of the GPU temperature after a full loading (98°C is 100% and 42°C is the 0%). In our case, the system took 29 seconds to reach 62°C (decreasing of 63%). We can determine a kind of cooling factor:
(98-62) / 29 = 1.24 °C/sec.

![]() ) AND when the Post Processing is checked. This bug is fixed in the version 1.0.7 and I’ll give more details on this bug when MSI will release the version 1.0.7. This bug has been reported in this thread.
) AND when the Post Processing is checked. This bug is fixed in the version 1.0.7 and I’ll give more details on this bug when MSI will release the version 1.0.7. This bug has been reported in this thread.